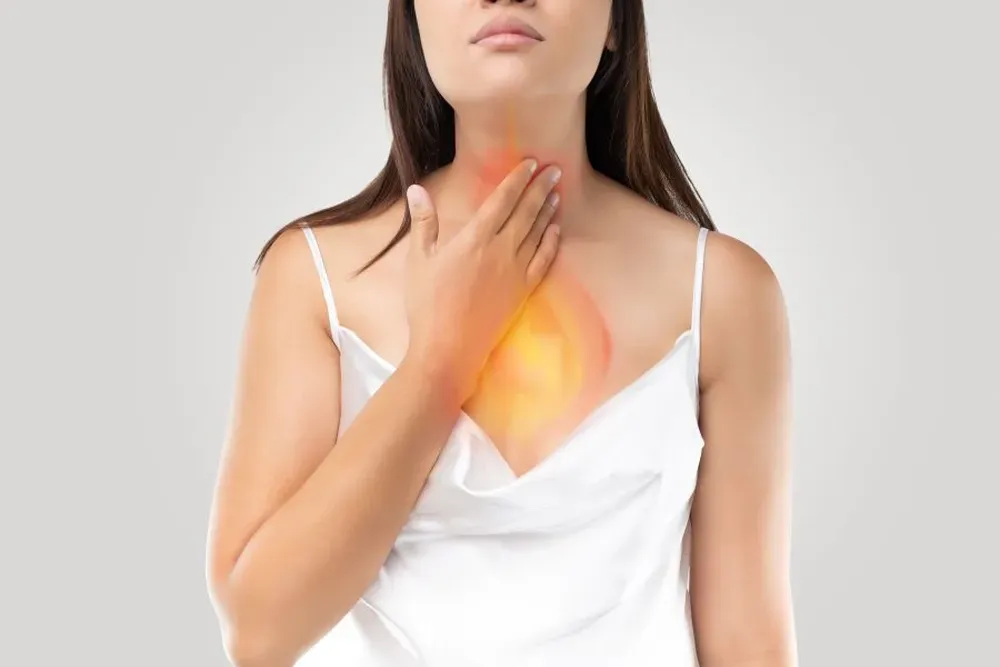
What Is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)?
GERD is a common digestive disorder affecting millions of people worldwide. It is a chronic condition where the stomach acid flows back into the oesophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. Common symptoms include heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest, and regurgitation, where stomach contents flow back into the throat. Understanding GERD is crucial for better health and managing its symptoms effectively.
What Causes GERD?
The digestive system is a complex process that breaks down food and absorbs nutrients. GERD occurs when the lower oesophageal sphincter (LES), a muscular ring between the oesophagus and the stomach, weakens or relaxes abnormally, allowing stomach acid to move upwards. Diet, lifestyle choices, and obesity can contribute to the development of GERD.

What Are the Symptoms of GERD?
The symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) can vary from person to person, but the most common ones include –
- Heartburn – A burning sensation in the chest, usually after eating or lying down. It may feel like a fiery discomfort that rises from the stomach to the chest and throat.
- Regurgitation – A sour or bitter taste in the back of the throat, accompanied by the sensation of stomach contents returning to the mouth.
- Chest Pain – Chest pain that may be mistaken for a heart attack. This pain is caused by the irritation of the oesophagus due to stomach acid.
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia) – Having a sensation of food getting stuck in the throat and progressive difficulty in getting food down the oesophagus.
- Chronic Cough – A persistent cough that is not related to a respiratory infection but is triggered by the irritation of the oesophagus by stomach acid.
- Sore Throat and Hoarseness – Frequent irritation can lead to a sore throat and hoarseness in the voice.
- Worsening Asthma Symptoms – In some cases, GERD can exacerbate asthma symptoms, leading to increased breathlessness and wheezing.
- Nausea and Vomiting – Some individuals with GERD may experience occasional nausea and vomiting.
Not everyone with GERD will experience all of these symptoms. Some individuals may have mild symptoms, while others may have more severe and frequent manifestations. If you suspect you have GERD or are experiencing persistent symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
How Is GERD Diagnosed?
If you experience persistent GERD symptoms, it’s essential to consult a doctor. They will review your medical history and perform a physical examination. Diagnostic tests, such as endoscopy and pH monitoring, may be conducted to confirm GERD and assess its severity.
What Are the Complications of Untreated GERD?
Untreated GERD can lead to several complications that may significantly impact your health and well-being. Some of the potential complications include –
- Esophagitis – This occurs when untreated GERD results in inflammation of the oesophagus. Repeated exposure to stomach acid can damage the delicate lining of the oesophagus, leading to pain, difficulty swallowing, and an increased risk of developing ulcers.
- Esophageal Ulcers – Untreated GERD can lead to the development of ulcers in the oesophagus, which can cause pain and risk of bleeding.
- Barrett’s Oesophagus – Barrett’s oesophagus occurs when long-term acid exposure result in changes to the lining of the oesophagus. This condition increases the risk of developing esophageal cancer hence vigilant follow-up is needed.
- Esophageal Stricture – Chronic inflammation of the oesophagus can cause scar tissue to form resulting in the narrowing of the oesophagus. This condition is known as oesophageal stricture which can cause difficulty swallowing and food getting stuck in the food pipe.
- Dental Caries – Repeated exposure to stomach acid can also affect dental health. The acid can erode tooth enamel, leading to tooth sensitivity, cavities, and other dental issues.
- Respiratory Complications – Aspiration of stomach contents into the lungs can lead to pneumonia or respiratory infections.
Can GERD Be Prevented?
While GERD might not be entirely preventable, certain lifestyle changes can reduce its occurrence and severity. This includes avoiding trigger foods, practising portion control, and elevating the head while sleeping to minimise acid reflux.
What Are the Medications for GERD?
Over-the-counter antacids provide temporary relief by neutralising stomach acid. Prescription medications, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2 blockers, reduce acid production in the stomach, offering long-term relief from GERD symptoms.
What Are the Tips and Precautions for Living with GERD?
Lifestyle plays a significant role in managing GERD symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise can alleviate pressure on the stomach. Lifestyle modifications such as avoiding triggering food, smoking cessation and avoiding nighttime snacking can help minimise GERD symptoms. Seeking support and educational resources on GERD management can lead to ideal outcomes and enhanced quality of life.