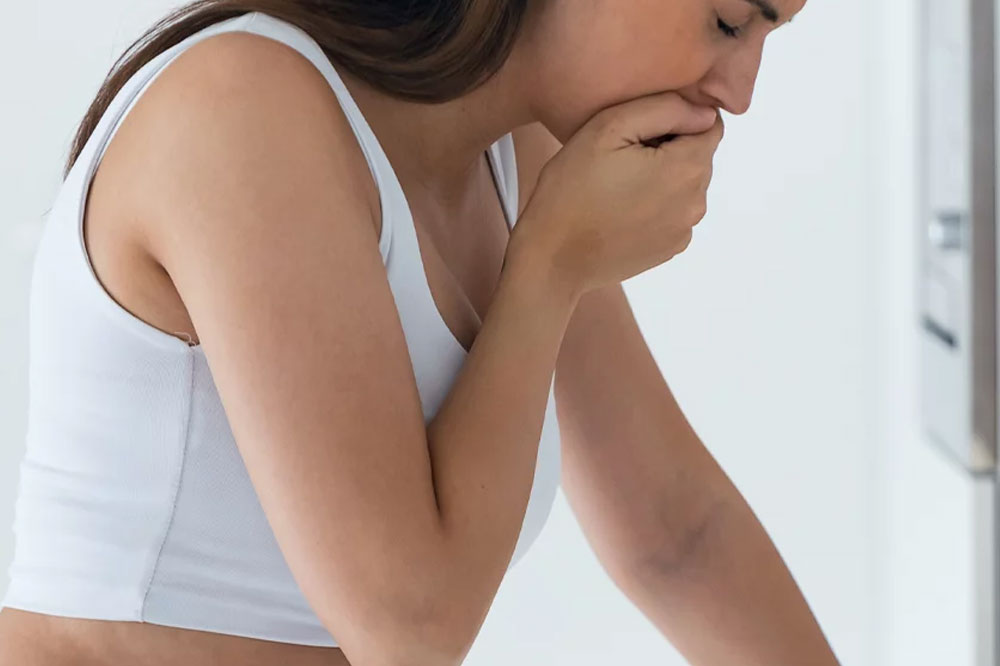
What Is Nausea/Vomiting?
Nausea is a queasy feeling in the stomach that often precedes vomiting. It’s a sensation that something is wrong within the body, making you feel like you might throw up. Vomiting, on the other hand, is the act of forcefully emptying the stomach contents through the mouth. The brain controls both of these responses and can be triggered by various internal and external factors. Various factors can cause these symptoms and may require medical attention depending on their severity and duration.
What Are the Common Causes of Nausea/Vomiting?
Various factors can cause nausea and vomiting. Some common causes include:
- Viral Infections – Viruses that affect the digestive system can lead to nausea and vomiting. These infections are often referred to as stomach flu or gastroenteritis.
- Food Poisoning – Consuming contaminated food or beverages contaminated with harmful bacteria, viruses, or parasites can trigger severe nausea and vomiting.
- Overeating – Consuming large amounts of food in a short period can overload the stomach and lead to feelings of nausea, which may result in vomiting to relieve the discomfort.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption – Drinking too much alcohol can irritate the stomach lining and cause nausea and vomiting as the body tries to expel the toxic substance.
- Medications – Certain medications, especially those known to irritate the stomach or affect the balance of chemicals in the brain, can induce nausea and vomiting as side effects.
- Pregnancy (Morning Sickness) – Many pregnant women experience nausea, often called morning sickness, especially during the first trimester.
- Emotional Stress – Strong emotions, anxiety, or fear can trigger a physical response, leading to feelings of nausea and the possibility of vomiting.
- Migraine Headaches – Severe migraines can accompany nausea and vomiting as part of the overall symptom complex.
- Gallbladder Problems – Issues with the gallbladder, such as gallstones or inflammation, can cause discomfort and nausea, particularly after eating fatty meals.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) – Chronic acid reflux, where stomach acid flows back into the oesophagus, can cause nausea and occasional vomiting.
- Peptic Ulcers – Open sores that develop on the stomach lining or small intestine can cause nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- Chemotherapy or Radiation Therapy – Cancer treatments can cause nausea and vomiting as side effects due to their impact on healthy cells and the gastrointestinal system.
When to Seek Medical Help?
While occasional nausea and vomiting are usually not cause for concern, certain circumstances warrant medical attention. You should seek help if:
- Vomiting lasts for more than 24 hours or is severe and persistent.
- You notice blood in your vomit or have vomit that looks like coffee grounds.
- Nausea and vomiting are accompanied by severe abdominal pain or intense headache.
- You experience signs of dehydration, such as excessive thirst, dark urine, or dizziness.
- There are other concerning symptoms like high fever, confusion, or rapid heartbeat.
What Are the Diagnostic Procedures to Identify Causes?
To determine the underlying cause of nausea and vomiting, doctors may perform various diagnostic procedures, including:
- Physical examination and medical history review.
- Blood tests to check for infections or other abnormalities.
- Imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds to visualise the internal organs.
- Endoscopy to examine the digestive tract.
- Urinalysis to assess kidney function and detect potential issues.
Why It's Important to Share Detailed Symptoms With the Doctor?
Sharing detailed symptoms with your doctor is crucial because nausea and vomiting indicate numerous health conditions. Understanding the specific nature, frequency, and accompanying symptoms can help doctors pinpoint the root cause more accurately.
This information allows for proper diagnosis and timely treatment, which is essential for managing any potential underlying issues effectively. Open communication with your doctor empowers them to provide you with the best possible care and helps ensure a faster recovery and improved overall well-being.