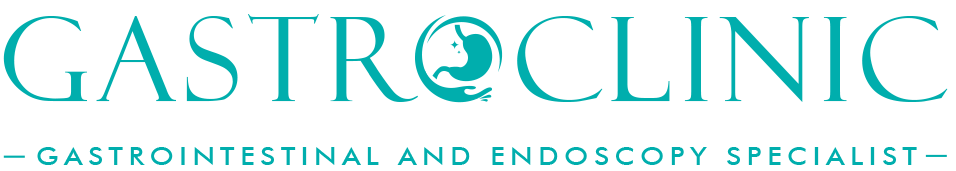What Is Acid Reflux?
Acid reflux, also known as heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a condition where stomach acid travels upwards into the oesophagus. The oesophagus is the tube that connects our throat to the stomach. Normally, a muscular valve called the lower oesophageal sphincter (LES) prevents the acid from moving up. When the LES becomes weakened or relaxes abnormally, acid can escape into the oesophagus, leading to a burning sensation in the chest or throat. While occasional acid reflux is normal, persistent or severe cases may require medical attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and when to seek help can lead to better management and relief.
What Are the Common Causes of Acid Reflux?
Several factors can contribute to the development of acid reflux. Some common causes include:
- Certain Foods – Spicy, fatty, or acidic foods can trigger acid reflux symptoms in susceptible individuals.
- Overeating – Consuming large meals or lying down immediately after eating can increase the risk of acid reflux.
- Obesity – Excess body weight can put pressure on the stomach, promoting acid reflux.
- Hiatal Hernia – This occurs when a part of the stomach pushes up into the chest through the diaphragm, affecting the LES’s function.
- Pregnancy – Hormonal changes and pressure on the abdomen during pregnancy can lead to acid reflux.
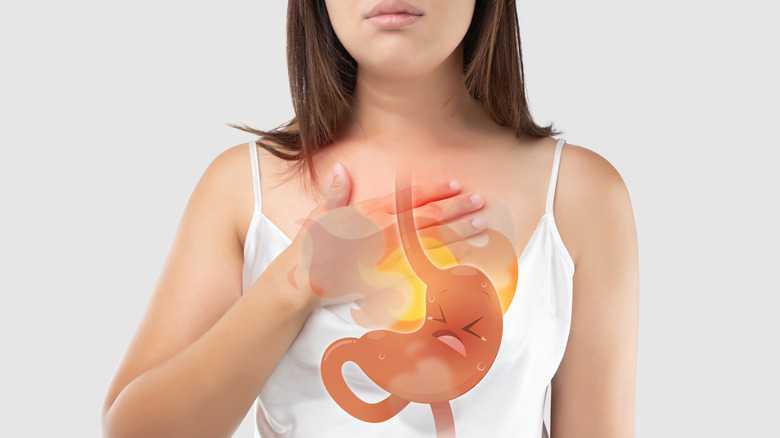
How Does Acid Reflux Feel Like?
Acid reflux typically feels like a burning sensation or discomfort in the chest, often referred to as heartburn. It is often described as a fiery or sour feeling that may rise from the stomach and move up towards the throat.
Some people may also experience regurgitation, where stomach contents flow back into the mouth, leading to a sour or bitter taste. This sensation can be distressing and may worsen after eating, lying down, or bending over.
In more severe cases, chronic acid reflux can cause additional symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, persistent coughing, or wheezing.
When to Seek Medical Help?
It is important to seek medical help for acid reflux if you experience any of the following situations:
- Frequent or Persistent Symptoms – If you frequently experience heartburn or acid reflux symptoms, even after making lifestyle changes or using over-the-counter medications, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
- Difficulty Swallowing – If you find it difficult to swallow or feel like food is getting stuck in your throat, it could be a sign of more severe acid reflux or complications that need medical attention.
- Unexplained Weight Loss or Loss of Appetite – Sudden weight loss or a loss of appetite without any apparent reason could indicate a more serious underlying issue and should be evaluated by a doctor.
- Chronic Cough or Wheezing – If you have a persistent cough or wheezing that does not seem to be related to other respiratory issues, acid reflux could be the cause.
- Chest Pain or Pressure – While heartburn is a common symptom of acid reflux, severe chest pain or pressure, especially radiating to the arm, neck, or jaw, should not be ignored. These symptoms could be indicative of more serious conditions, including a heart attack, and require immediate medical attention.
- Symptoms Interfering with Daily Life – If acid reflux symptoms are significantly impacting your daily activities, work, or sleep, it’s essential to seek medical help for proper evaluation and management.
- Taking Medications Long-Term – If you have been relying on over-the-counter medications for an extended period to manage acid reflux, it’s advisable to consult a doctor. Long-term use of some medications can have side effects and may not address the root cause of the problem.
What Are the Diagnostic Procedures to Identify Causes?
To diagnose the underlying causes of acid reflux, a doctor may recommend the following:
- Gastroscopy – Also known as oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD) or upper endoscopy. This test uses a flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) that is inserted through the mouth to visualise the oesophagus and stomach, looking for any abnormalities.
- pH Monitoring – This test measures the level of acidity in the oesophagus over 24 hours to assess acid reflux patterns.
- Esophageal Manometry – This test evaluates the strength and function of the oesophagal muscles and LES.
- X-rays or CT scans – These imaging tests can help identify hiatal hernias or structural issues.
Why It’s Important to Share Detailed Symptoms With the Doctor?
Openly discussing detailed symptoms with the doctor is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective acid reflux treatment. Since various factors can cause acid reflux, understanding the specific triggers and patterns helps the doctor tailor a personalised treatment plan. Early detection and proper management can prevent complications and improve the overall quality of life for individuals dealing with acid reflux.